Jazz Music and Mathematics Summary
The article discusses the topic Jazz Music and Mathematics. It dives into the subtopics such as durations of notes in jazz and swing conventions, number of bars in a passage, jazz notes, jazz chords, and symphonic and jazz keys and instrumentation.
Note duration is defined as the length of a played note. The jazz notes’ durations are different from symphonic music which is determined by binary fractions. Let a whole duration be t, the other duration is fractions of t. However, ties and triplets are also used for complex durations or non-terminating binary fractions.
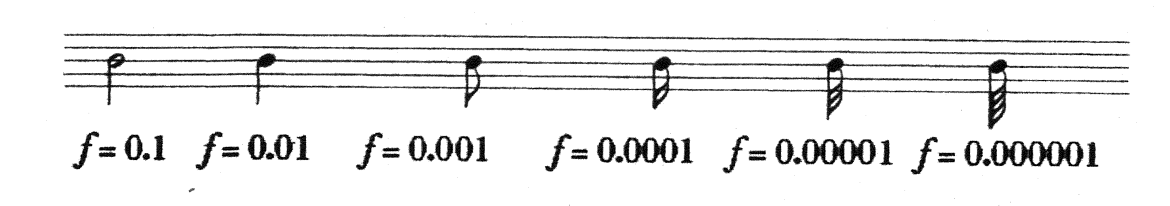
Jazz notes’ durations are classified as straight bars and swing bars. Bars in music are defined as segments which are divided by vertical lines. Straight bars are the same as symphonic durations, which are determined by binary fractions. On the other hand the swing bars are determined by two conventions. This notation facilitates jazz writing. Triplets are represented by two eighth notes while a sixteenth note follows a dotted eighth note. Swing rhythm is divided unequally which allows jazz music to have its improvisational characteristics and make it more flexible for the musicians.

Another distinctive trait of jazz are the blue notes. Blue notes are a blend of major and minor keys to create a unique emotion. While the major chords create a cheerful feeling due to its effect on the brain whilst the minor chords create a melancholy feeling.
Jazz chords are flexible especially in comparison to symphonic music. In jazz music instead of the regular major chord which includes the notes C, E, and G is replaced by the basic sixth chord which adds the note A to the regular major chord. Chords are three or more notes played together which builds a harmony. Jazz music also uses extended chords which have between seven and thirteen notes.
Instrumentation is another aspect that differs between jazz music and symphonic music. Symphonic music prefers sharp keys and accordingly tuned instruments. However, for jazz music flat keys are favorable and the instruments are naturally oriented. While violins and flutes can be tuned and used for symphonic music, saxophones and trumpets are self oriented and used for jazz music. Although there are still instruments which are used for both genres such as trumpets. This separation also indicates the historical development of both genres.
Douglas Maurer, W. The Mathematics of Jazz. archive.bridgesmathart.org/2004/bridges2004-273.pdf.
Quigley, Nick. “What Is Swing? Getting inside the Sound We All Love - Jazz Music Institute.” Jazz Music Institute, 24 June 2024, www.jazz.qld.edu.au/what-is-swing-getting-inside-the-sound-we-all-love/#:~:text=At%20the%20heart%20of%20Jazz,that%20drives%20the%20music%20forward. Accessed 13 Jan. 2025.
to, Contributors. “Arrangements of Pitches or Chords to Induce a Hierarchy of Perceived Relations, Stabilities, and Attractions.” Wikipedia.org, Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., 25 Aug. 2003, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tonality. Accessed 13 Jan. 2025.
to, Contributors. “Musical Chord Extending a Simple Triad.” Wikipedia.org, Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., 12 Jan. 2004, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_chord. Accessed 13 Jan. 2025.
to, Contributors. “Time Unit in Rhythmic Musical Notation.” Wikipedia.org, Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., 4 Dec. 2003, en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bar_(music). Accessed 13 Jan. 2025.
“Why Are Minor Chords Sad and Major Chords Happy?” BBC Science Focus Magazine, 3 July 2022, www.sciencefocus.com/science/why-are-minor-chords-sad-and-major-chords-happy. Accessed 13 Jan. 2025.